Most of us use anti-virus on a regular basis, we have completely trusted it with our personal information and online transaction. We let it scan all data on our computers without worrying about privacy or data theft. Antivirus detects and removes harmful intrusive software which can damage or destroy computer system. But, have you wondered what an antivirus actually is and how it works? Why do we have to update it frequently? These are the questions we are going to discuss in this article.
But before we discuss about “ANTI-VIRUS” we should know the different types of intrusive software which can harm computer systems. We need to understand how these harmful software work, only then we can understand how Antivirus detects and removes them.
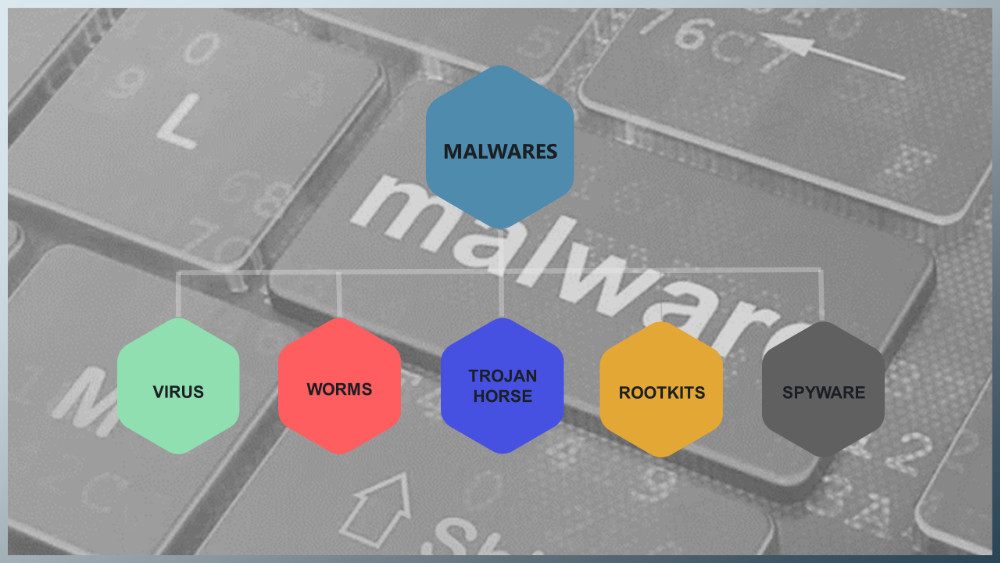
What is a MALWARE (Malicious Software)?
Malware is a contraction for Malicious Software. Any kind of computer contaminant is called as malware i.e. anything which can interfere with the proper functioning of computer can be characterized as a MALWARE.
A few important contestants are briefly discussed here:
VIRUS
These are small programs which manipulate data without the knowledge of the user. In 1980’s viruses were simpler, they just tend to copy themselves on the system over & over again ultimately crashing the system. Virus requires the user to run the executable file or open the document to which it is attached in order to corrupt the system.
WORMS
Worm works same as virus, attack the healthy computer and corrupt it, the difference lies, the way they propagate through the network. WORMS “actively” transmit themselves over the network, i.e. they don’t require user’s intervention in order to propagate.
TROJAN HORSE
By Greek mythology, Trojan horse was a wooden horse built by the Greeks, disguised as the trophy of victory for Troy. Actually it was used to smuggle Greek troops inside the city. In the same way this malware is disguised as a useful & harmless program and attracts the user to download it. Once its inside, it attaches to the healthy files, corrupting them.
A point should be noted that TROJAN HORSE requires “user interference in order to propagate” just like the virus do.
ROOTKITS
These are the programs which are designed to manipulate user’s operating system so that it would not detect its presence, for this, ROOTKITS are activated at the time of boot up. They are very dangerous due to their stealth and capability to take administrative control over a computer.
SPYWARE
SPYWARES are designed to keep tabs on your personal information such as passwords, browsing history, personal identification documents, communications, etc.
Vocabulary for Malwares and Antivirus
Now we will discuss some important terms which will help to understand malware & anti-virus better. Here, just the introduction is provided, they will be covered thoroughly in upcoming articles.
SIGNATURE
In this case, it implies that every kind of malware has some specific characteristics in their coding, which can be used for their detection. It’s like using photograph of criminals at airport in order to match them with the people and detect someone suspicious.
ZERO DAY THREATS / MALWARE
These are the malwares whose signature is not yet known.
SANDBOX
This is a security method to run suspicious or un-trusted programs under isolated virtual environment so that program’s behavior could be checked.
BACKDOOR
These malware bypass the normal authentication process such as passwords in order to retrieve sensitive information without the knowledge of the user.
FALSE POSITIVE
It is a situation when anti-virus identifies a non-infected file as malware and flags it.
ZOMBIE COMPUTERS
The computers which have network access and can be controlled remotely without the knowledge of the user are called zombie computers. Simply speaking they are the computers which are hacked and used for illegal activities by the hacker to cover-up its own identity.
SPAM
These are the unwanted mails which are generally send in bulk to hinder the performance of target server or computer by clogging and crashing it(Denial of service attacks). DOS attacks utilizes spamming through zombie computers in order to crash the target website or system by clogging the server so that intended users could not have access to the website or server.
BUGS
Bugs are the un-intentional errors in the program which hinder with the functionality of the system.
What is an Antivirus?
These are the programs which are used to detect and stop the spread of malwares. Antivirus software are designed to prevent, search, detect, and remove malwares. In 1987, when US Defence Department communication network (ARPANET) came under attack of virus, it was clear that a computer software was required to protect the network from such attacks.
Antivirus software run continuously in background on user’s computer. It scan data such as webpages, files, software, USB devices to detect and eradicate malwares as quickly as possible.
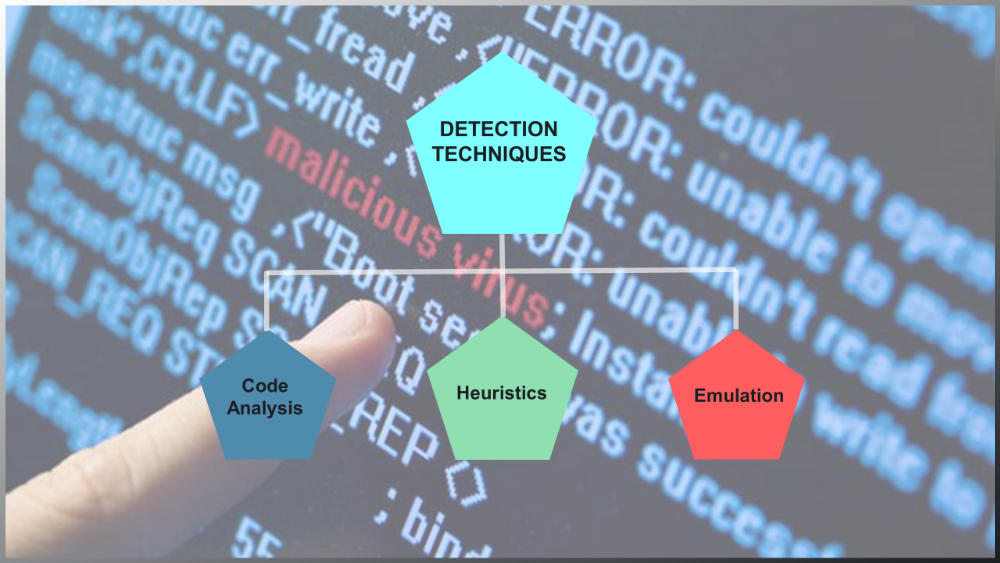
How does an Antivirus work?
Some simple techniques used by ANTI-VIRUS for MALWARE detection are:
CODE ANALYSIS
The anti-virus runs each file and matches it with the existing database of malware signature, if a match is found the file is flagged. This is a lengthy task but most of the anti-virus software uses it, this procedure does not provide protection against ZERO DAY THREATS since their signature is not available. To keep the signature database up-to-date anti-virus requires frequent updates.
HEURISTIC APPROACH
Some malwares tend to disintegrate themselves in order to pass code analysis. To detect such malwares, antivirus forms a family of malwares on the basis of some common properties in the code.
EMULATION
This procedure utilizes the “SANDBOX” in order to run the suspicious file in a safe and isolated environment to check its behavior. If it performs unauthorized tasks it is flagged as a malware and is removed.
SOME USEFUL FACTS
- BOB THOMAS wrote an experimental self replicating program called CREEPER in 1971.
- PERVADE ANIMAL represents the 1st Trojan horse released in 1975.
- FRED COHEN was the first person to publish an academic paper on computer virus in 1984. Then in 1988 he published a demonstration that it is not possible for an algorithm to detect every kind of virus.
I hope you gained some insightful information about malwares and antivirus. Don’t forget to share this article if you found it interesting.